



Why BLDC for ceiling fan?
Today the typical ceiling fan is based on AC motors which are power hungry. Along with this the typical AC motor based fans have the rpm control through the capacitor or resistor based regulators and is not efficient as there is loss in the regulator itself to some extent. In addition the RPM control is by controlling the voltage and the voltage fluctuations of the mains make it very challenging to have constant RPM based on the AC mains supply. Further, existing AC motor solution, results in power factor (PF) degradation with no improvement for PF and there are other ill effects like harmonics injection to the AC mains, etc.
The total amount of air flow or displacement is based on the blade size & rpm and does not change due to any other factor. The proposed solution is to keep the same air flow or displacement with less of energy usage along with improving the PF using the BLDC motor based ceiling fans.
Typical BLDC motor based ceiling fan has much better efficiency and excellent constant RPM control as it operates out of fixed DC voltage. The proposed BLDC motor and the control electronics operates out of 24V DC through an SMPS having input AC which can vary from 90V to 270V. A comparison between BLDC and conventional ceiling fans is shown below (42” ceiling fan is considered).
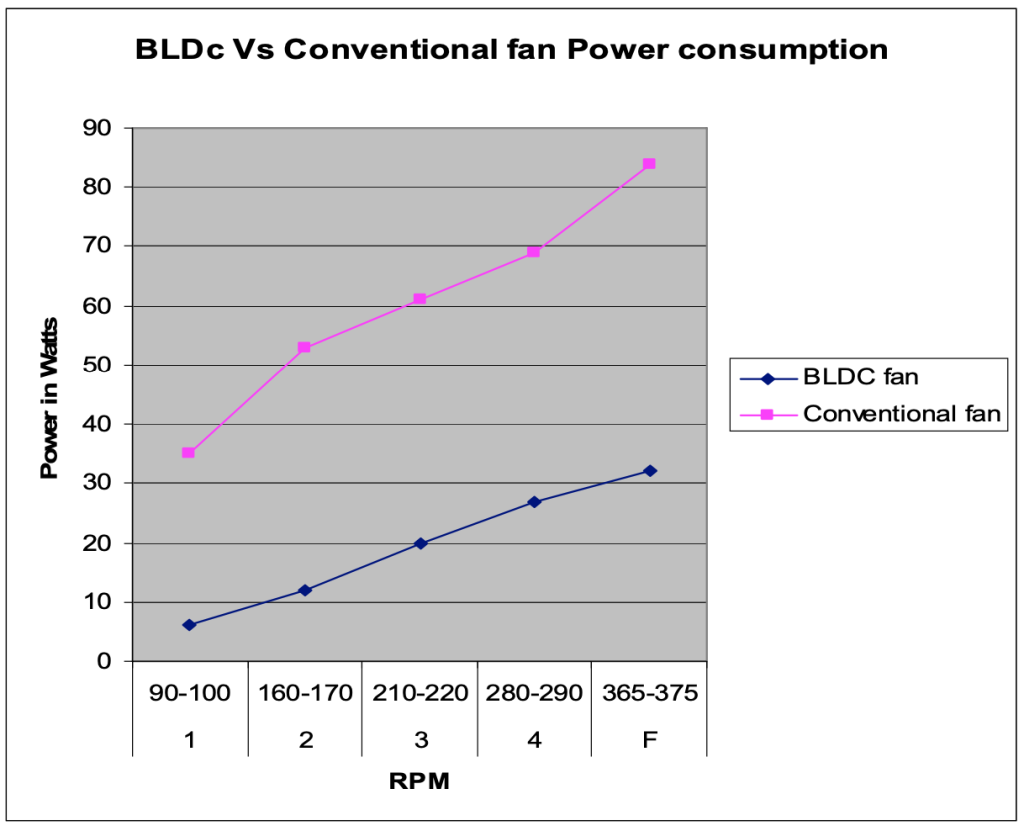
The power consumption is less than half at full speed and is about 20% at low speed for the BLDC motor compared to the conventional motor based ceiling fan, as can be seen from the graph above. The Power Supply (PS) used is at 85% efficiency and the electronics consumes less than 0.5W. The power curves for the BLDC ceiling fan considers the total power consumed from the wall socket.
The mechanical energy required to rotate at full speed (typically 360rpm) for a 42” conventional ceiling fan is about 0.65Newton Meter. The equivalent electrical energy, as per the below equation, would be around 26Watts, considering about 95% efficiency for mechanical to electrical energy conversion. The total power consumption of 32 watts as seen in the above design seems to be with in the design boundaries for such a motor.